Battery Basics
Battery Basics Archive
Are you brand new to the world of batteries? No problem! We have a collection of articles to help explain the battery basics, if you have any questions please feel free to reach out to us!
Battery Banks: Wiring Batteries in Parallel and Series
Using a bank of batteries provides an increase in voltage when they are wired together in a series. Connecting them in parallel boosts both the total current capacity and the overall amp-hour capacity. Doing so means that the needs of those applications that require more amperage, voltage or both can be met by wiring batteries together instead of investing in a larger and heavier battery.
How to wire up a battery bank
There are two main ways that batteries can be wired: in a series or parallel to each other. While the process to wire them together is basically the same — use jumper wire to connect the appropriate terminals — the procedure differs depending on which method is being used.
- Wiring up batteries in series
By wiring batteries in a series, voltage is increased but the overall amp-hour capacity does not. The amp-hour rating on each battery in a series bank must be the same.
Connecting batteries in a series means placing one right after another. To be effective, the battery terminals must be placed in the correct order. The positive end of one battery needs to be wired to the negative end of the one that is next in the series.
Use jumper wire to connect the terminals of the batteries in the series. Then use a set of cables to connect the open negative and positive terminals to the application. Using batteries with the same capacity rating and voltage keeps any potential charging problems to a minimum and won't impact battery life.
- Wiring up batteries in parallel
In contrast to wiring batteries in a series, those in parallel increase both overall amp-hour capacity and total current capacity. This last increase is accomplished by a decrease in total resistance. In a parallel bank, each battery must have an identical voltage rating.
Because the batteries amperage is increased during a parallel connection, it's likely that a heavy-duty cable will be necessary. Otherwise, the cable might burn out.
Wire up batteries in parallel by connecting both positive terminals with a jumper wire. Use a different jumper wire to connect both negative terminals to each other. In order to keep the batteries equalized, connect to the positive at one end of the battery bank and the negative at the other. However, it is possible to connect the application to one of the batteries and it will still drain both equally.
- Using a combination of series and parallel
It's also possible to wire batteries together in both a parallel and series configuration. By doing so, both the amp/hour rating and voltage output are increased. Four batteries are required in order to wire them together in this manner.
Wire the batteries up in parallel first before joining them together to form a series. Only a single cable is needed because it acts as the bridge between the positive and negative terminals of two separate parallel banks. This is acceptable if a terminal has more than one cable attached to it.
Theoretically, it's possible to wire together as many batteries as desired — though this could result in a confusing and unsafe situation. To keep track of connections, particularly those that are complex and that involve a number of batteries and cables, make a diagram of the battery banks prior to constructing them. Doing so could increase safety and reduce confusion.
What is the difference between a deep cycle and starting battery?
What is a Deep Cycle Battery?
A deep cycle battery is designed to provide reliable power down to the 80% depth of discharge (DOD) level. The battery will be able to be discharged down to this level time after time with no or minimal loss of capacity. Deep cycle batteries are constructed with thicker solid lead plates which reduces the instant starting power of the battery, but enables it to handle the constant cycling.
Due to the plate design of the battery, true deep cycle batteries will normally have a much lower CCA rating than their starting counterparts. A few vendors with true deep cycle battery offerings are Vision, Crown, CSB, and NorthStar.
The overall life span of a deep cycle battery has an inverse correlation with the depth of discharge - see below: 
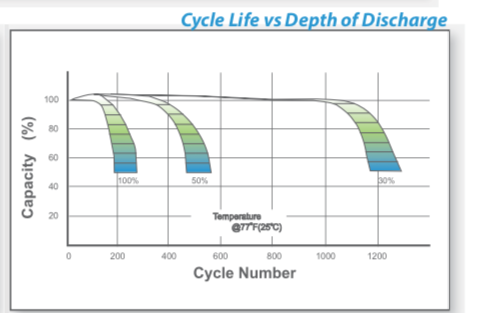
As you can see by the above chart, this battery will have an increased cycle life at a lower DOD. Most manufacturers recommend running your deep cycle battery setup down to the 50% DOD mark for the best bang for your buck.
What is a Starting Battery?
A starting or cranking battery is designed to deliver a large burst of power for a short period of time. The plate structure of the everyday starting battery also differs greatly from that of the deep cycle. The starting battery plates will be much thinner and a sponge like texture instead of a thick solid plate. The reason behind this is that the sponge like material is porous and gives a very large surface area for the active material to generate power.
A starting battery will only be discharged between 2 and 4% on average when the vehicle is started and have well over a 1000 cycles before the battery experiences capacity loss. The downside to the thin sponge like plate of the starting batteries is that they are not designed to withstand cycling below that 2 to 4% mark. If a starting battery is deep cycled it will begin to rapidly shed the sponge like material on its plates and loose capacity, in reality you have about 100 to 125 cycles of 50% DOD in a starting battery before it begins to deteriorate.
In Conclusion
The main difference between a starting battery and a deepcycle battery comes down the the construction of the plates. The deep cycle battery will have fewer but thicker solid lead plates that will product low instant starting power but consistant long term power. The starting battery has many more plates that are thinner and porous enabling it to produce a strong instant power for a brief period of time which rapidly diminishes the longer the battery is cycled.
